Natural gas will continue as the top fuel source for U.S. electricity generation and carbon emissions will fall to the lowest point since 1988, according to federal data released this week. In its Short Term Energy Outlook, the Energy Information Administration projects domestic natural gas production and consumption increases over the next year, largely driven by gains in Appalachia.
The EIA’s energy production and use forecast comes on the heels of an Independent Fiscal Office report identifying Pennsylvania and Texas as leading the country in natural gas production growth over the past decade. As a result of abundant, affordable natural gas, more than $13 billion in private capital has been invested in Pennsylvania to build upwards of 20 new, clean combined-cycle natural gas power plants that will reliably power millions of homes.
And with natural gas generating more than a third of U.S. electricity, “U.S. carbon emissions have mostly declined since peaking at 6,003 million tonnes in 2007,” Reuters reports.
Key takeaways from EIA’s report include:
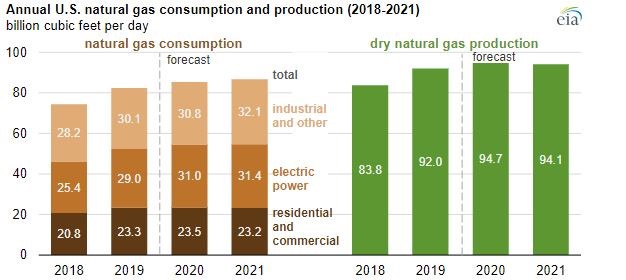
- Consumption Increase: “Total domestic U.S. natural gas consumption averaged an estimated 85.3 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) in 2019, and EIA expects it will increase by 1.4 Bcf/d (1.7%) in 2020.”
- Production Growth: “EIA estimates that dry natural gas production in the United States will average 94.7 Bcf/d in 2020, up 2.9% from 2019.”
- Lowest CO2 Emissions Since 1988: “After decreasing by 2.1% in 2019, EIA forecasts that energy-related carbon dioxide emissions will decrease by 2.0% in 2020 and decrease by 1.5% in 2021.”
The monthly report attributes the nation’s production and consumption growth to improved drilling efficiency and increased takeaway pipeline capacity, which primarily comes from the Appalachian Basin. Forecasted growth is also supported by planned expansions in liquefied natural gas capacity and exports.
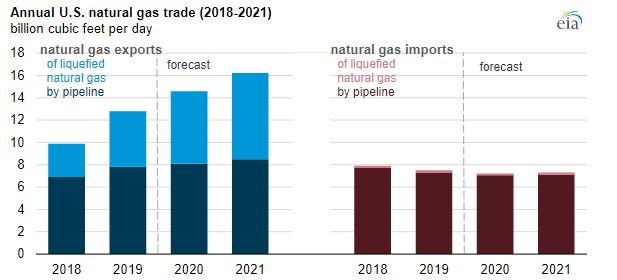
Rising LNG exports have transformed the United States into a net exporter for the first time since the 1950s. The EIA suggests natural gas exports via pipeline will continue to increase as more infrastructure is built for transportation, contributing to the anticipated 8.8% boost in gross pipeline exports by 2021.
- Electric Power Sector Use: “The largest natural gas consuming sector in the United States is the electric power sector. EIA estimates that electric generation consumed an average 31.0 Bcf/d in 2019, up 7.0% from 2018 because of new natural gas-fired electric generation capacity and competitive natural gas prices.”
- Manufacturing Sector Use: “EIA forecasts U.S. industrial sector consumption of natural gas to rise by 4.6% in 2020. Most of the 2020 increase in the forecast is the result of new chemical projects. Low natural gas prices in recent years have made it economical to increase use of natural gas as feedstock in ammonia for nitrogenous fertilizer and methanol manufacturers.”